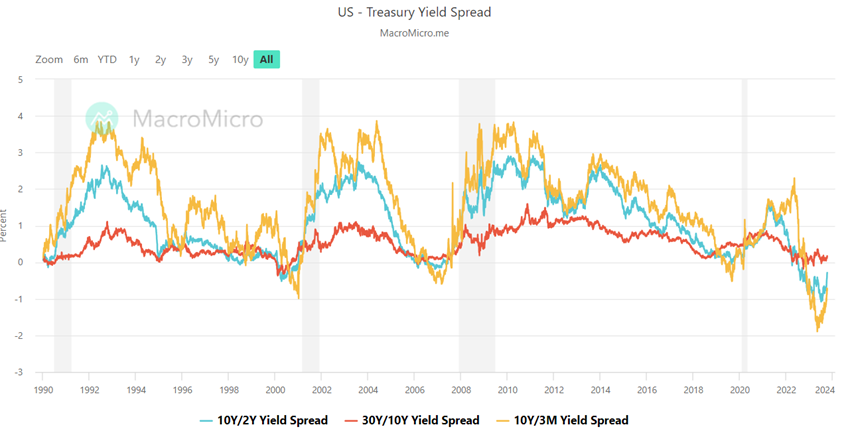
Yield Curve Turned Much Less Inverted. What Does It Mean?
Recently, the yield curve became much less inverted than it was months ago, though it's not fully uninverted yet, with most short-dated yields still above long-dated yields.
We know that the term spreads often reflect changes in the economic cycle. Term spreads tend to rise during recessionary periods and fall during expansionary periods. An inverted yield curve, which the US has experienced for approximately one year, typically signals an impending recession. However, in previous instances, it has taken one year or longer after the inversion for an economic downturn to occur, making timing predictions challenging.
Consequently, analysts now rely on another indicator: the uninversion of the yield curve. This approach makes sense intuitively because as the economy approaches a contraction, markets anticipate a series of rate cuts and bet that the Fed will ease policy to address the slowdown.
■ Term spreads show a positive correlation with the unemployment rate
The economic cycle can be reflected in the unemployment rate. Higher unemployment apparently means a weaker economy, which suppresses short-term interest rates. The unemployment rate reached 3.8% in September, up from last year's lowest point of 3.4%. If the weakening labor market trend continues, term spreads may become even less inverted or even turn positive.

JOLTS and nonfarm payroll data released this week seem contractionary. However, the JOLTS data always lagged behind. Although job openings increased to 9.61 million in August, up from 8.92 million in the previous month, the Indeed website showed that working opportunities decreased again in September.

Nonfarm payroll data is also confusing. The increase in the number of part-time workers suggests that there may be duplication of data on Nonfarm payrolls, which exaggerates the tightness of the labor market.
■ Is the evidence robust over time?
An informal way to assess the robustness of yield curve forecasts of real activity is to examine the ex-post accuracy of the results. In some cases, as with the regularity that yield curve inversions and uninversions precede recessions, the evidence is immediate and quite consistent, as in the United States since 1960. The only apparent miss was in 1967, when the economy experienced a “credit crunch” that the NBER did not classify as a recession, despite a marked decline in industrial production.
■ What is the relationship between yield spread and the stock market?
Based on the S&P500, during the period from 1956 to the present, the inversion of the yield curve occurred 9 times. There were 6 times that the yield curve inverted before the stock market had reached its peak. The average time between the initial inversion and the S&P 500's relative peak was 10.57 months from the 1970s, according to Nasdaq Inc.


Disclaimer: Moomoo Technologies Inc. is providing this content for information and educational use only.
Read more
Comment
Sign in to post a comment
71791308 : Not this time. Heading ti a depression
safri_moomoor : ok now
William LEW : This means that the world's chives (bonds) will be cut, and the next harvest period (stock market) will begin again
Tyson Ricch : It hard to trust the process
RJBoy : The recession is waiting around the corner ready to strike.