Tesla Q4 2023 Earnings Preview: Gross Margin Expected to Remain Under Pressure
I. Key Focus Areas of Tesla's Business
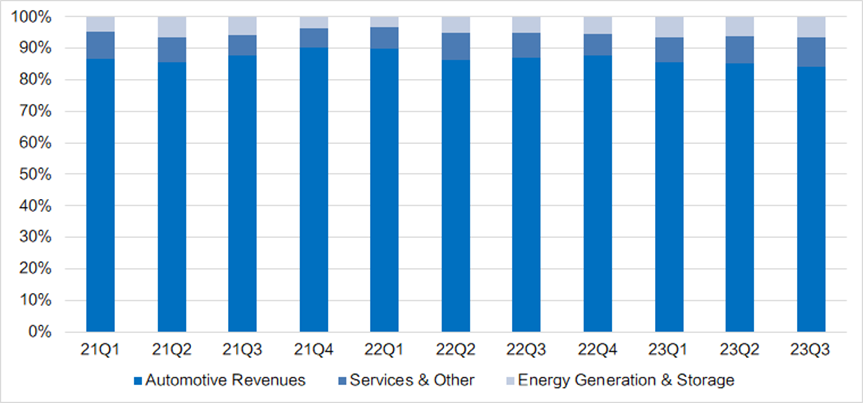
Tesla's business structure is mainly divided into three major divisions: Automotive, Energy, and Services and Other.
The Automotive division includes revenue from electric vehicle sales, leasing income, and the sale of regulatory credits;
The Services and Other division includes non-warranty after-sales services, paid charging services, and used car sales.
In terms of revenue share, sales of electric vehicles and related automotive services account for over 95%.
Tesla's other businesses such as FSD (Full Self-Driving), DOJO, and robotics have great potential in the medium to long term and have contributed significantly to Tesla's valuation. However, electric vehicle sales remain the core foundation of the business.
Figure: Tesla's Main Business Revenue Structure (%)
Key Focus Areas for Tesla's Quarterly Earnings Report:
1) Revenue side: Since the sales volume for the fourth quarter has already been announced, the decisive factor for revenue will be the change in Average Selling Price (ASP) per car. Since Tesla's pricing strategy varied across different regions during the fourth quarter, the final change in ASP will determine if revenue exceeds expectations.
2) Profit side: Gross margin remains the most closely watched metric. There are many factors that affected the gross margin in the fourth quarter, both positive and negative, and there is uncertainty regarding the actual performance of the gross margin.
3) Guidance for 2024: This includes targets for sales volume in 2024, progress on the production of the Cybertruck, plans for the next-generation vehicle platform, etc.
II. Low Likelihood of Revenue Exceeding Expectations
In the fourth quarter, Tesla's production and sales were slightly higher than expected, with approximately 495,000 vehicles produced and more than 484,000 delivered, an 11% increase from the previous quarter. This resulted in a total delivery volume of 1.81 million vehicles for 2023, a 38% year-over-year increase, surpassing its previously set target of 1.8 million vehicles. Although delivery numbers reached a historical high, the fourth quarter only just met the target, and the market's response to this news was relatively muted.
Additionally, the high sales volume in the fourth quarter was partly influenced by consumers purchasing vehicles ahead of time to benefit from tax relief. Starting January 2024, new regulations for battery procurement in the United States took effect, leading to the loss of the $7,500 tax credit eligibility for Tesla's all-wheel-drive version of the Cybertruck and some Tesla Model 3 variants.
Figure: Tesla's Quarterly Sales Volume (Units)

From the perspective of revenue per vehicle, due to the strategy of price reductions, Tesla's revenue per vehicle is expected to decrease slightly quarter-over-quarter in the fourth quarter. In the fourth quarter, Tesla implemented a price reduction strategy for its two main models, the Model 3 and Model Y, in the U.S. region, with a reduction of about 3%. Starting in October, the starting price for the standard version of the Model 3 was reduced from the previous $40,240 to $38,990, the long-range version from $47,240 to $45,990, and the performance version from $53,240 to $50,990. The price increases for the mainstream Model 3 and Model Y variants in China partially offset these reductions, with smaller increases (but there was another price cut in the first quarter).
Compared to the consensus estimates from Bloomberg, Tesla is expected to report fourth-quarter revenue of $25.786 billion, a 6% increase year-over-year, with automotive sales revenue of $20.86 billion, a 12% increase quarter-over-quarter, and Q4 vehicle deliveries up 11.4% quarter-over-quarter. Due to inconsistent price adjustment directions in different regions, there is uncertainty in the ASP. However, considering that changes in tax policy in the U.S. may drive more sales growth this quarter and that the price reduction was significant, it is expected that the ASP will be flat or slightly down quarter-over-quarter. We believe there is a low likelihood of Tesla exceeding revenue expectations.
Figure: Tesla Automotive Revenue Per Vehicle (Tens of Thousands of USD)

III. Gross Margin Continues to Be Under Pressure
Over the past six quarters, Tesla's gross profit per vehicle has decreased from $17,865 to $8,431, a decline of as much as 53%; the automotive business gross margin (excluding regulatory credit sales) has continuously declined from 18.96% in Q1 2023 to 16.33% in Q3 2023. The company-wide overall gross margin has also decreased from 19.3% in Q1 2023 to 17.9% in Q3 2023.
Figure: Automotive Business Gross Margin (Excluding Regulatory Credits)

This quarter, Tesla's gross margin is influenced by several positive and negative factors:
1) Price cuts for main models in the US region – negative, significant
2) On the raw material cost front, lithium carbonate prices showed an overall downward trend in the fourth quarter – positive, minor
3) The third quarter saw an increase in per-vehicle depreciation costs due to factory shutdowns, while the fourth quarter returned to normalized production – positive, minor
4) Increased productivity at the Berlin and Texas factories – positive, minor
According to Bloomberg consensus estimates, Tesla's overall gross margin for Q4 2023 is expected to be 18.09%, compared to 17.9% in the previous quarter. Although there are some favorable factors this quarter, the negative impact of price cuts on the gross margin is significant, so the gross margin is expected to remain under pressure, staying roughly flat or slightly down from the previous quarter.
IV. Persistent Risk Factors for 2024
1) The competitive landscape is becoming more intense, and there is market concern about Tesla brand fatigue and a lack of new car models
Tesla's two most important markets, the United States and China, are both facing trends of increasing competition. In Q4 2023, BYD sold 526,409 pure electric vehicles, which is more than 40,000 units above Tesla's sales, officially surpassing Tesla to become the world's top-selling pure electric vehicle brand.
In the Chinese market, the penetration rate of new energy vehicles in 2023 has already exceeded 30%, but the growth rate of pure electric penetration has significantly slowed down. The 200,000 to 400,000 RMB mid-to-high-end price range, which is Tesla's segment, is one of the most competitive segments. In 2024, new challenger brands such as Huawei's AITO and Li Auto are planning to launch several new car models.
In the U.S. market, changes in the competitive landscape and penetration rates have been relatively slow, and Tesla still holds a dominant market share. However, the sales data from 2023 indicates that traditional automakers like Ford and General Motors, which are transitioning to new energy, are making strides into the electric vehicle market. Last year, under the backdrop of significant price cuts by Tesla, it was primarily hybrid vehicles that captured Tesla's market share. A decline in Tesla's market share in the future is a likely event.
Figure: Electric Vehicle Sales by Brand in the U.S. Market, in Millions of Units

Competitors are becoming increasingly aggressive, and in comparison, Tesla has made only minor updates to its existing models last year and has not released any blockbuster new models in the short term. Concerns about Tesla brand fatigue and a lack of new models are causing market worries that the strong offensive from competitors could impact the demand for Tesla vehicles.
2) Cancellation of Tax Incentives
The United States introduced new electric vehicle subsidies in 2023, but the situation reversed in 2024, leading to Tesla losing subsidies for the Model 3 SR and Model 3 LR. Germany's electric vehicle subsidy program was originally set to last until the end of 2024 but was also ended early this year. The high base of sales growth in 2023, driven by price cuts and increased subsidies in Europe and the US, makes growth in 2024 more challenging.
3) Price Cuts Expected to Continue
Tesla started the year with another round of price cuts in Europe and China. In China, prices for the Model 3 and Model Y were reduced, with the Model 3 Standard Range Plus's price cut by 15,500 RMB to 245,900 RMB, and the Long Range version's price cut by 11,500 RMB to 285,900 RMB, both reductions being about 6%; the Model Y Rear-Wheel Drive version was reduced by 7,500 RMB to 258,900 RMB, a reduction of about 3%.
In Europe, due to the reduction in subsidies, Tesla also lowered prices in Germany, France, and the Netherlands, with the Long Range and Performance versions of the Model Y in Germany seeing price reductions of 9% and 8.1%, respectively. Although Tesla has not formally reduced prices in the United States, nearly all of Tesla's inventory has a discount of 10% or more.
With Tesla's increased supply and price cuts, the depreciation rate of Tesla's used car values is faster than that of its competitors' vehicles, and the used car market will in turn affect the demand for new vehicles.
Figure: Tesla Used Car Price Trend

This means that price wars are expected to continue in 2024, and pressure on average selling prices (ASPs) and gross margins will persist. The delivery of the Cybertruck in 2024 will further negatively impact gross margins, as the cash flow for the Cybertruck is expected to be negative over the next 18 months.
4) Rising Labor Costs
After the U.S. auto industry union triumphed over the three major car manufacturers last year, the Big Three raised their employees' wages by 25%. Under industry pressure, Tesla also announced a pay raise for all its U.S. production workers, approximately a 10% increase in worker wages (there may be a second wage adjustment in the future, but the final adjustment scale is currently uncertain). Tesla has about 130,000 employees globally, with about half in the United States. The rise in labor costs will negatively affect Tesla's gross margin in 2024.
Other short-term risk factors include: the stoppage of production at the Berlin Gigafactory due to a red tide attack, cancellation of orders by Hertz, and battles over voting rights by Musk, among others.
V. Significant Valuation Pressure
In summary, we believe that it is unlikely that Tesla's revenue performance will exceed expectations, as gross margins are under pressure and there is considerable uncertainty regarding stock performance after the financial report. From a valuation perspective, as of Q3 2023, Tesla generated $2.3 billion in free cash flow and realized a net profit of $7.1 billion. Considering the increase in sales but pressure on profits in Q4, it is estimated that Tesla could realize a net profit of $9.1 billion and free cash flow of $3.2 billion for the full year 2023. As of January 22, 2024, Tesla's current valuation is $663.7 billion, which is equivalent to 70 times the net profit and over 200 times the free cash flow of 2023, indicating a high valuation.
Tesla faces many risk factors that could suppress revenue and profits in 2024, with bleak guidance for the year ahead. The possibility of rapidly digesting the high valuation through growth next year is relatively low, and it is difficult to relieve the pressure on its valuation before these risk factors are clarified. In the short term, without the support of core electric vehicle sales, imaginative businesses such as AI, FSD (Robotaxi), Dojo, and Optimus will also struggle to realize their valuations.
So, what mid-term factors could help reverse Tesla's current predicament?
1) The launch of the next-generation production platform and economy car models: According to information currently circulating about Tesla, after the new platform goes into production, it will significantly reduce vehicle production costs, relieving Tesla from the dilemma of gross margin issues. The emergence of Tesla models priced below 200,000 RMB could also be possible, and the introduction of lower price tiers could become Tesla's next growth driver.
2) Unexpected production increases for Cybertruck: Musk previously cut Cybertruck's sales expectations due to the impact of 4680 battery production capacity. Deliveries are expected to be limited before production capacity expands in 2024, with an estimated 250,000 units not delivered until 2025. The Cybertruck has significant halo effects with considerable reservations currently limited by insufficient production capacity. Based on U.S. 2022 vehicle sales, half of the top 10 selling models are pickups, indicating substantial demand potential. If deliveries exceed expectations in 2024, it could be an effective path to drive performance.
3) Massive growth in FSD users: Tesla still has a clear lead in the intelligent driving field, with FSD mileage growing rapidly, surpassing 500 million miles in Q3. Combined with sales advantages, Tesla has accumulated a large amount of data that can be used for training. Reports indicate that Tesla's FSD is about to be launched in China, priced at around 64,000 RMB, which is double the price of EAP.
In the long run, as time progresses, many of Tesla's new businesses that have yet to be monetized are expected to gradually come to fruition. Tesla's business model will become increasingly diversified, and with Musk's strong ability to generate buzz, Tesla's current predicament is awaiting the realization of more catalysts.
Disclaimer: Community is offered by Moomoo Technologies Inc. and is for educational purposes only.
Read more
Comment
Sign in to post a comment
SPACELIGHT : You should know.
ZnWC : In the short run, the market is a voting machine but in the long run, it is a weighing machine.
Tesla Q4 2023 Earnings Review
https://www.moomoo.com/community/feed/111814110347270?global_content=%7B%22invite%22%3A%22101709443%22%2C%22promote_content%22%3A%22mm%3Afeed%3A111814110347270%22%7D&data_ticket=212ca245a589f1e400fb2e247953bc77&futusource=nnq_personal_host