Q1 In the Ningde era, revenue declined, but profit increased
On the evening of April 15, Ningde Times, a leading power battery company, announced its results for the first quarter of 2024. Investors are concerned that against the backdrop of negative revenue growth, Ningde experienced a positive increase of 18.56% after deducting non-net profit.
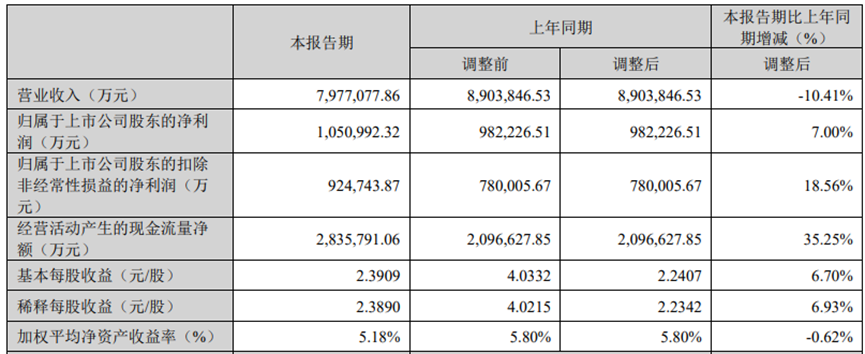
In the first quarter of 2024, Ningde Era achieved operating income of 79.8 billion yuan, down 10.4% year on year and 24.9% month on month; net profit to mother was 10.5 billion yuan, up 7% year on year, down 19% month on month; gross margin reached 26.42%, up 5.15 percentage points year on year; net interest rate was 14.03%, up 2.71 percentage points year on year; and Ningde Era's net cash flow from operating activities reached 28.36 billion yuan, an increase of 35.25% over the same period in 2023.
The battery price war continued in the first quarter, and it is no surprise that revenue declined during the Ningde era. However, benefiting from falling raw material prices and strict cost control measures, profit and gross margin levels remained positive during the Ningde era.
1. Q1 revenue declined, but profit increased
In the first quarter of this year, the phenomenon of negative revenue growth in the Ningde era continued. According to Wall Street News and Insight Research, the battery installed volume and market share increased in the first quarter of the Ningde era, so the main reason for the decline in revenue was due to a fierce battery price war.
In the first quarter of this year, the price war became even more intense. The average price of lithium iron phosphate cells (power type) fell to 0.38 yuan/Wh, 13.6% month-on-month, 52% year-on-year; ternary lithium batteries (power type) fell to 0.48 yuan/Wh, 4% month-on-month, and 44% year-on-year.
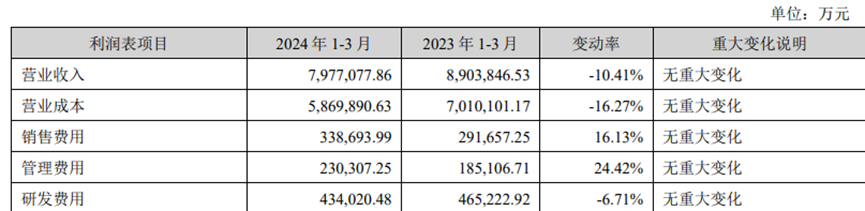
Fortunately, cost control was excellent during the Ningde era. The operating cost for the first quarter of this year was only 58.7 billion yuan, a decrease of 16% at the same time. The decline in operating costs was greater than the decline in operating income. It was also the first time in the last three years during the Ningde era that there was a year-on-year decline in costs. The main reason is that the procurement cost of raw materials has dropped more than the price of batteries (the price of lithium carbonate has decreased by 55%). Some of the raw materials in the Ningde era were owned mines, while others were ordered by Changxie, and the cost was lower than the spot price.
This also led to a different trend of deducting non-profit and revenue in the Ningde era. Deducting non-profit returned to positive growth, reaching a growth rate of 18%, totaling 9.247 billion yuan.
In addition to controlling operating costs, capital expenditure during the Ningde era also showed signs of slowing down. In 24Q1, fixed assets in the Ningde era were 114.5 billion yuan, showing a month-on-month decline for the first time. Projects under construction were 26.22 billion yuan, a year-on-year decline of 18.9%. However, during the conference call, the company mentioned that short-term signs of capital expenditure are not obvious, and it is hoped that they can be compared through annual data.
2. The power battery market at home and abroad had a double harvest in the Q1 Ningde era
In the first quarter of this year, the leading Ningde era not only continued to grow in overseas markets, but the domestic market share also returned to around 50%. The increase in shipment volume partially offset the negative impact of falling prices, so even during the most difficult quarter, the decline in operating income was not serious.
In January-February of this year, the global power battery installed capacity of the Ningde Era reached 35.5 GWh, a year-on-year increase of 44.9%, and the market share increased 4.8 percentage points to 38.4%. The overall proportion of overseas power batteries installed has reached 27.4%, and the year-on-year growth rate has almost doubled, far exceeding its growth rate in the domestic market.

In addition to this, domestic market share, which had been sluggish throughout last year during the Ningde era, also began to recover. The installed power battery capacity of the Ningde Era in the first quarter of this year was 41.31 GWh, up 41% year on year, and the market share increased 4 percentage points year on year to 48.93%.

However, it is worth noting that judging from the accounts receivable turnover ratio and contract debt in the first quarter of the Ningde era, the overall order level and industry position declined in the first quarter.
In the first quarter of 2024, the contract debt of the Ningde era was 20.6 billion yuan, a decrease of 2,038 billion yuan compared to the same period last year. This is also the first time in nearly three years that the Ningde era experienced a negative year-on-year increase in contract debt; the receivables turnover ratio was 1.35, which is also a new low in the past three years.
3. From product export to technology licensing
From 2021 to 2023, the overseas market share of Chinese power battery manufacturers grew rapidly, from 18% to 33.9%.
However, in terms of breakthroughs in overseas markets, Ningde is currently facing some resistance. Therefore, the technology licensing model has become a way for Ningde to break through today.
Under this model, Ningde Times directly licenses battery manufacturing technology to partners and provides corresponding services. The company charges royalties and service fees.
Since it does not involve too much investment in plant construction or raw material costs, etc., the initial investment in such asset-light businesses is small, and the gross margin level is even more impressive.
Furthermore, the Ningde Era has continued to invest in research and development. In the first quarter of this year, R&D expenses in the Ningde era were 4.34 billion yuan, an increase of 24.71% over the previous year, a slight decrease of 6.7% over the previous year, but mainly the price of R&D materials fell. The company said during the conference call that the investment intensity of R&D personnel was only getting higher and higher.
Currently, Ningde Times is exploring the possibility of technical licensing cooperation with more than 10 European and American automobile companies. Among them, it has already begun preliminary cooperation with the three major overseas automobile giants Ford, General Motors, and Tesla on technology licensing models.
Specifically, the power battery factory that Ford and Ningde invested 3.5 billion US dollars to build in southwestern Michigan in the US is still progressing in an orderly manner. Although construction of the battery factory was temporarily suspended during this period due to changes and obstructions in US policy, the normal progress of cooperation has now resumed.
As the first technical licensing cooperation, if the cooperation between the Ningde Era and Ford succeeds, it will undoubtedly provide a new way for the Ningde era to expand in the global market. It will also have a great reference effect on the subsequent cooperation and construction of Chinese power battery manufacturers and even material manufacturers in the US.
GM is also planning to jointly build a lithium iron phosphate power battery plant with Ningde Era in North America, and production capacity will not be lower than the scale of previous cooperation between Ningde Era and Ford. The Ningde Era also does not own shares in cooperatively built battery factories, but instead charges patent licensing fees and service fees. If Ford's cooperation is successfully implemented, GM's cooperation will not have any problems.
Tesla also hopes to adopt a technology licensing model and cooperate with Ningde to develop a new generation of ultra-rechargeable batteries, new products, or manufacture them at Tesla's Nevada plant.
In the first quarter when demand for terminals was poor and competitors' price wars were frequent, the Ningde era, which was the leader, withstood the pressure. Despite a decline in revenue, profits bucked the trend.
Whether technology licensing can help the Ningde era's overseas development will be the next focus of market attention.
