SMIC(00981.HK) Earnings Preview: Linger at Industry Cycle Bottom, Downstream Demand as Key Driver
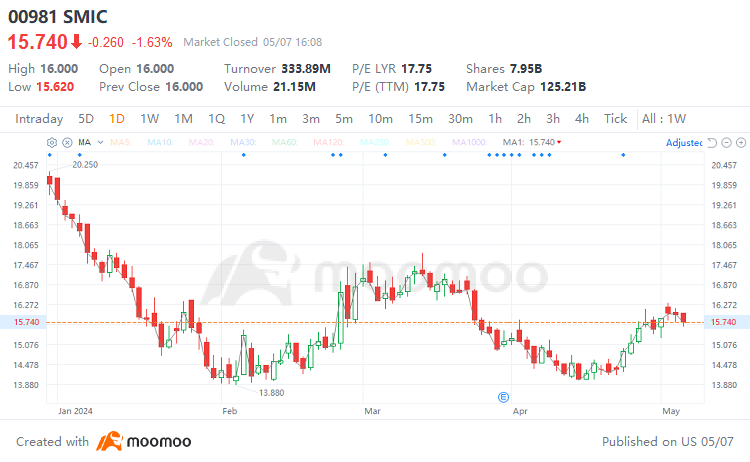
$SMIC(00981.HK$ is set to release its first-quarter earnings report on Thursday, May 9th. Since the beginning of the year, the company's stock price has decreased by 20.8%, underperforming the Hang Seng Index's gain of 8.4%, indicating a lackluster performance. In the current semiconductor cycle, how will SMIC's performance play out?
I. Business Composition
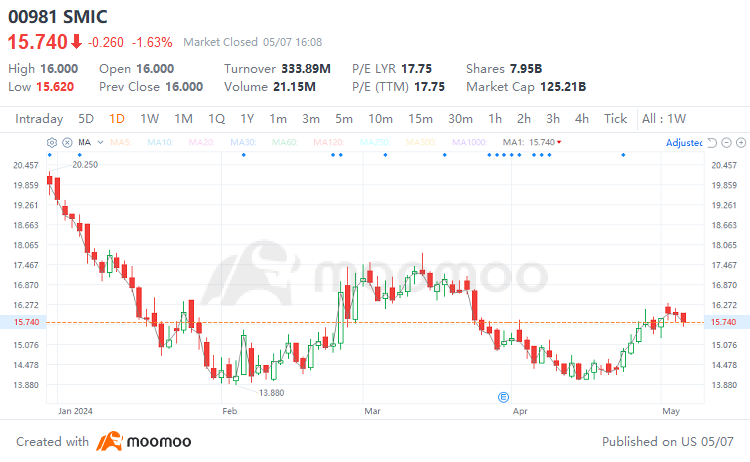
The main business of SMIC is wafer foundry services, which accounted for 91.66% of the company's revenue in 2023, with the highest level of technology offered being the 14-nanometer advanced process. In addition, SMIC provides other services such as photomask and testing. Meanwhile, due to a series of sanctions imposed by the U.S. government on Chinese high-tech companies, SMIC's revenue share from the U.S. market has been declining year by year, with revenues dropping from 40% to 16%, while domestic revenues have returned to over 80%.
The annual performance report for 2023 shows that the company's total revenue was $6.32 billion, a decrease of 13.1% compared to the previous year; unaudited net profit was $900 million, down 50.4% from $1.82 billion in 2022. However, the company demonstrated resilience in adversity, with fourth-quarter revenue reaching $1.68 billion, exceeding market expectations, and achieving a year-over-year increase of 5.08% and a quarter-over-quarter improvement of 3.2%.
II. The Industry is at the Bottom of the Cycle, with Downstream Demand Recovering
The semiconductor industry is a typical cyclical industry, with a cycle length of about four years. The upward phase usually lasts for 2 to 3 years, while the downward phase lasts for 1 to 1.5 years. The current cycle's downward interval has been from the second quarter of 2022 to the present. The industry is currently slowly recovering from the bottom of the cycle, with future industry focus shifting towards demand forecasting and product structure optimization.
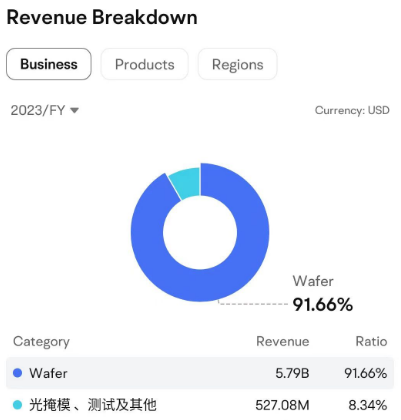
The current state of the industry cycle can be glimpsed from upstream silicon wafer shipments. According to the Semiconductor Industry Association (SEMI), shipments of silicon wafers of all sizes declined in the first quarter due to the continued decrease in the operating rate of IC foundries and inventory adjustments. In the first quarter, global silicon wafer shipments dropped to 2.834 billion square inches, a quarter-over-quarter decrease of 5.4% and a year-over-year decrease of 13.2%, with the pace of capacity recovery falling short of expectations.
Chart: Global Silicon Wafer Shipments in the First Quarter (Billion Square Inches)
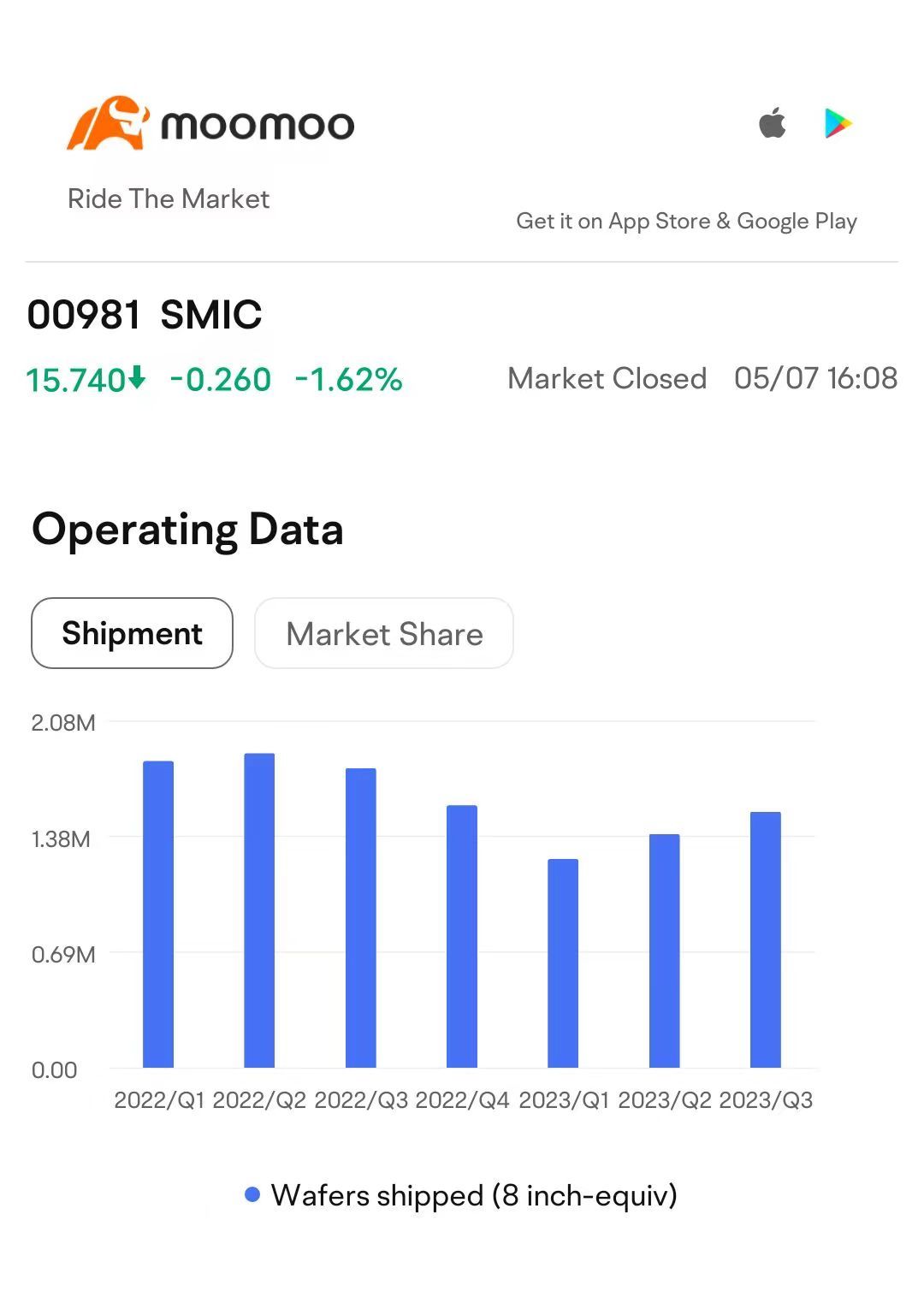
It is worth noting that even during the industry downturn, SMIC continued to expand. Since the bottom of the first quarter of 2023, its capacity utilization rate gradually rebounded and stabilized between 76% and 78%. In the fourth quarter of 2023, SMIC expanded its capacity to 805,500 wafers per month (calculated on an 8-inch wafer equivalent basis), outpacing competitors such as UMC in this expansion. However, on the whole, the average capacity utilization rate was lower than in 2022, with a decrease in the number of wafer sales and changes in the product mix affecting the performance of the financial report.
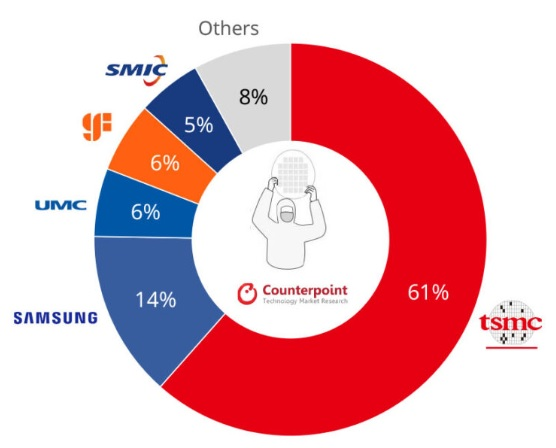
According to the latest market research by Counterpoint, SMIC's global foundry market share slipped from 6% in the third quarter to 5% in the fourth quarter of 2023, ranking fifth. Additionally, the foundry industry's revenue increased by about 10% quarter-over-quarter, but decreased by 3.5% year-over-year.
Chart: Global Foundry Market Share in the Fourth Quarter of 2023
In the consumer electronics sector, according to data from Canalys, with the recovery of the global macroeconomy and a resurgence in consumer demand, global smartphone shipments in the first quarter of 2024 saw a year-over-year increase of 11%. The Chinese market's growth rate at the beginning of the year was below the global average, but it warmed up for the first time in two years, with shipments remaining flat compared to the same period last year, reaching 67.7 million units.
III. Revenue Expected to Grow, High Inventory Impacts Gross Margin
Revenue Situation
Looking ahead to the first quarter of 2024, SMIC has provided guidance for a sequential revenue increase of 2%, which suggests that the company is expected to achieve revenues of $1.71 billion in the next quarter, slightly above the market consensus estimate of $1.69 billion.
Analyzing from the perspective of revenue = shipment volume * price, there are no clear signs of a rebound in prices. However, since the beginning of the year, some downstream customers have had significant needs to restock and prepare inventories, thereby driving an increase in the company's shipment volumes. For example, companies related to the manufacturing of Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) that support and connect electronic components have recently reported strong performance. Additionally, with the economic recovery, consumer electronics are experiencing a revival. Therefore, we assess that the company's revenue will be slightly higher than guidance, driven by downstream demand.
Chart: Company Wafer Shipment Volume Trend
Gross Margin
In the fourth quarter of 2023, SMIC's gross margin was 16.4%. By breaking down the cost structure, we can analyze the reasons for the change in SMIC's gross margin for this quarter:
Gross profit per wafer = Revenue per wafer - Fixed cost per wafer - Variable cost per wafer
1) Revenue per wafer: This quarter, SMIC's revenue per wafer (8-inch equivalent) was $1002, a sequential decrease of $53 per wafer.
2) Fixed cost per wafer (depreciation and amortization): The fixed cost per wafer (8-inch equivalent) this quarter was $360, a sequential increase of $22 per wafer.
3) Variable cost per wafer (other manufacturing expenses): The variable cost per wafer (8-inch equivalent) this quarter was $478, a sequential decrease of $30 per wafer.
4) Gross profit per wafer: SMIC's gross profit per wafer (8-inch equivalent) this quarter was $164, a sequential decrease of $45 per wafer.
The cost breakdown reveals that SMIC's gross margin decline from the previous quarter was mainly due to a drop in unit revenue and an increase in unit fixed costs. With increased capital expenditure, the company saw an increase in depreciation and amortization, indicating that counter-cyclical expansion further pressured the company's gross margin.
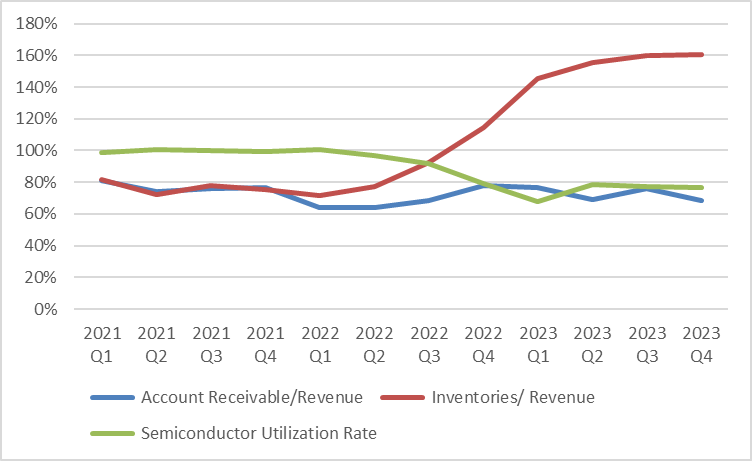
Additionally, looking at the company's inventory and accounts receivable, the inventory/revenue ratio has increased, and accounts receivable/revenue ratio has been fluctuating. Combined with the company's inventory and capacity utilization data, we can discern the company's trend. In the first quarter of 2022, the company was operating near full capacity, but subsequently, inventory levels continued to rise while capacity utilization began to decline. If the inventory is not effectively digested in the future, the capacity utilization rate is expected to remain at a relatively low level.
Chart: Operating Data Situation
Company management guidance indicates that the gross margin for the first quarter will be in the range of 9% to 11%, almost halving from 20.8% in Q1 of 2023, while the capital expenditure for 2024 is expected to be roughly flat compared to 2023. However, given the positive downstream demand, it is quite possible that management's gross margin guidance is conservative, and profitability could exceed expectations.
Expense Side
From the perspective of operating expenses, there has been a reduction in the past few quarters. Breaking down the operating expenses for Q4 of 2023, we see that research and development expenses were $189 million, general and administrative expenses were $148 million, and sales and marketing expenses were $9 million. The increase in administrative expenses is mainly due to the increased expenses associated with the opening of new factories.
IV. Stock Price Judgment and Investment Value Analysis
EPS
Current consensus expectations from Bloomberg forecast that the company's Q1 2024 revenue will grow by 15.6% year-over-year to $1.69 billion, with EPS decreasing by 57.78% year-over-year to $0.01. Based on the recovery in downstream sectors such as consumer electronics and PCBs, we predict that management's gross margin guidance may be conservative and that the company's performance will slightly exceed expectations.
Valuation
Currently, the company's PE ratio on the Hong Kong stock market is 17.75x, which is not cheap compared to the Hang Seng Index's current PE of 9.44x.
Shareholder Return
In terms of dividends, the company has no significant history of payouts, and given the substantial capital expenditures in recent years, the likelihood of announcing new buyback programs seems limited. Therefore, the company's performance in terms of shareholder returns is not impressive.
Conclusion
In summary, the company's revenue for the new quarter is expected to grow, but management has provided conservative gross margin guidance. Considering the current AI boom and the positive performance in downstream sectors such as consumer electronics and PCBs in the first quarter, there is reason to believe that the performance may slightly exceed expectations, offering some upside potential for the stock price.
Disclaimer: Community is offered by Moomoo Technologies Inc. and is for educational purposes only.
Read more
Comment
Sign in to post a comment